Blockchain Technology And The Future Of HR
Blockchain Technology And The Future Of HR
Over The Past Couple Of Years, There Has Been A Great Deal Of Chatter About “fintech” Or Financial Technology. One Category That Gets Plenty Of Buzz Is Bitcoin And Blockchain. What Is Blockchain? What Is Bitcoin (either With A Capital “B” Or Small “b”) And What Impact Will It Have On The World Of Recruitment? The Purpose Of This Blog Post Is To Answer Those Questions And Delve A Bit Into This New Technology And Highlight The Potential Real-world Implications For Human Resources.
What Is Blockchain Anyways?
Bitcoin Was Created In 2008 By An Anonymous Programmer Named Satoshi Nakamoto. No One Knows His Or Her Real Name And Whether It Is One Person Or A Group Of People.
Bitcoin is A Cryptocurrency Or Digital Money With Embedded Encryption Features. Think Of It As Money That Has Internal Safeguards Against Counterfeiting Or Double Spending. Bitcoin Uses Blockchain As A Method Of Transferring Value Between Market Participants. Generally Speaking Bitcoin With A Capital B Is A Specific Type Of Cryptocurrency (there Are Others Such As Ethereum And Litecoin). When People Refer To Bitcoin, With A Small “b” It Can Either Mean One Unit Of Bitcoin Or As A Generic Reference To All Cryptocurrencies.
Imagine That Bitcoin Is The Automobile And Blockchain As The Modern Interstate System. There Were Roads Before The Modern Car, But They Didn’t Have Sophisticated Tunnels, Tollways Or ERP Systems To Manage Traffic Flow. Similarly, There Are Vehicles That Exist Now, Due In Part To The New Modern Interstate System (e.g. Safety Features Like Guard Rails, Banked Turns, And Speed Bumps Were Only Introduced As Cars Moved Faster). There Will Also Be Future Vehicles (e.g., Autonomous Cars, Buses, Electric Cars) Which Use The Same Road System.
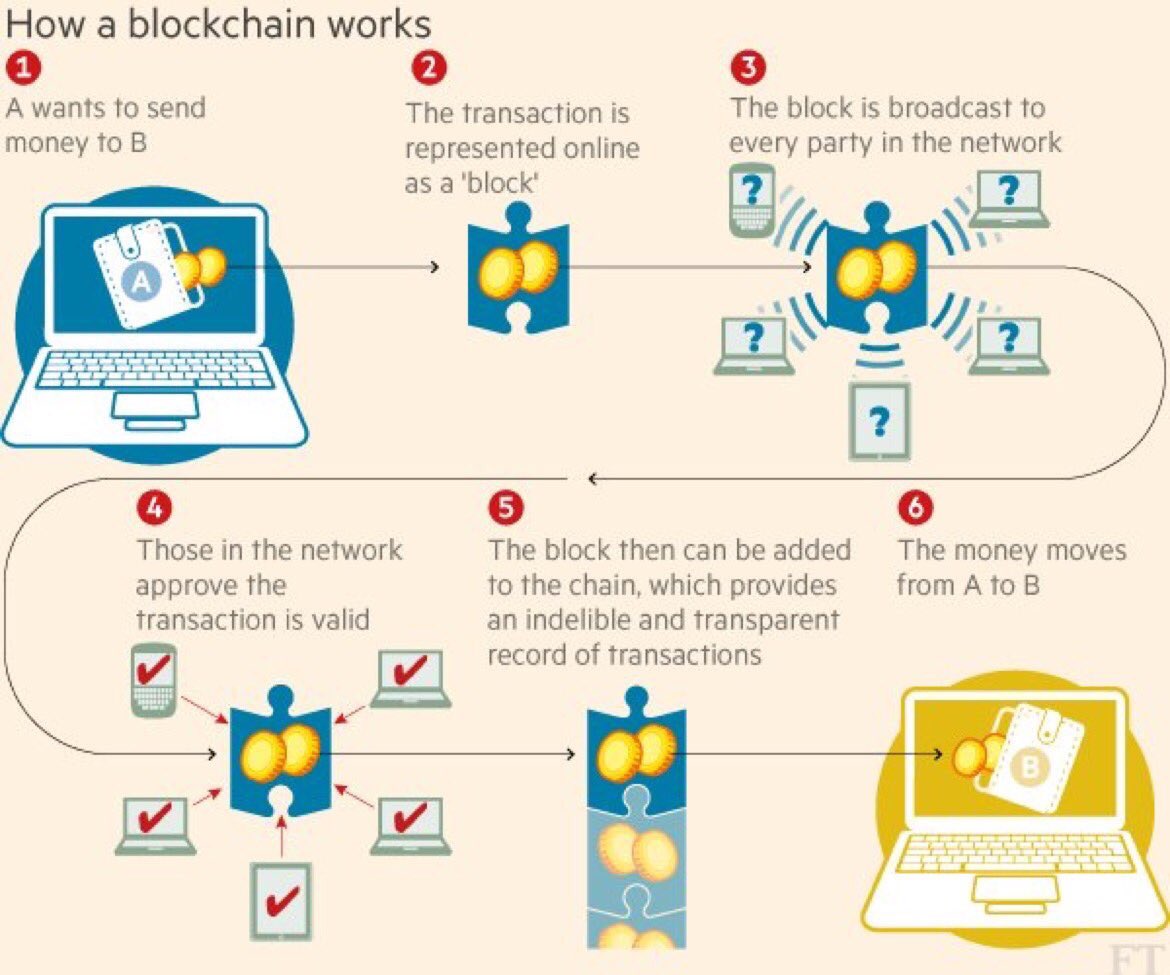
Source: Financial Times
These Future Vehicles Won’t Necessarily Rely On Internal Combustion Engines Driven By People. In The Same Way, The Blockchain Is A Platform Or System Of Protocols Which Will Allow Other Applications Besides Bitcoin.
Another Useful And More Relevant Analogy Is To Think Of Blockchain As TCP/IP protocol For The Internet. Nowadays, People Have Built Multimillion Dollar Companies On The Internet Without Needed To Understand The Exact Protocols. You Can Develop An Idea For A Marketplace Or Delivery Service That Would Have Been Virtually Impossible Last Century.
Uber, Amazon, AirBnB Would Not Have Existed 20 Years Ago Without The Confluence Of High-speed Internet Connections And Mobile Devices. In The Same Way, Businesses Of The Future May Rely On Blockchain Features Without Necessarily Getting Into The Technical Aspects Of It. Focusing On The Consumer And Resolving The Pain And Reducing The Friction Involved In Transactions Has Built Alibaba And Square Into Billion Dollar Companies.
For Further Evidence Of The Importance Of Technology In The Modern Business Era, Simply Look At The 5 Largest Companies By Market Capitalization In 2016 Vs 2011. It’s Clear Visually By Looking At The Green Colored Tech Boxes That They Have Come To Dominate The Modern Economy.
Source: Visual Capitalist
It’s Entirely Plausible That In 10 Years Time, We Will Stop Using “tech” As A Way To Distinguish Companies. In The Same Way That “digital Marketing” Is Being More Commonly Referred To As Simply “marketing”, Tech Companies Will Begin To Branch Into All Sorts Of Sectors. From This Perspective, We Will Use Industry Concentration To Distinguish Apple From Facebook.
However, For The Time-being, It Seems That Traditional Brick-and-mortar Companies Operated In Discrete Industry Verticals. What Distinguishes Them Most From Tech Companies Is A Narrow Focus On Industry And Lack Of A Technology Platform As A Key Competitive Advantage.
Distributed Ledgers
The Key Functionality Of Blockchain Is To Allow Multiple Parties Simultaneous Access To A True View Of The World Or Of Ownership. Without Going Into Too Much Detail, The Basic Underpinning Is That Everyone On The Blockchain Has A Copy Of Ownership And Can Verify This In Real-time.
A Traditional Ledger Or Balance-sheet Ultimately Has One Owner. Even After It Is Published, Only Company XYZ Can Say Whether Their Assets Are What They Say They Are. When Company XYZ Says Their Assets For The Prior Year Need To Be Restated From USD100 To USD90, They Tell All Interested Parties (banks, Vendors, Regulators, Etc…) And Everyone Else Agrees. The Other Parties Can Run Tests And Re-create Their Own Balance Sheets, But Ultimately The “truth” Is Relative.
What Makes Blockchain Technology Unique For Now Is That Tampering With The Records Is Virtually Impossible Due To How “blocks” Are Added To The “chain”. Each Block Is A Transaction Or A Transfer Of Some Type Of Value. Since Everyone In The Network Has To Implicitly Validate The Transaction (even If They Are Not A Party To It), Fraud Is Extremely Unlikely To Happen.
In This Sense, There Are As Many Copies Of The Ledger As There Are Participants. Unlike Copies In The Past Where There Was One Parent Ledger And Multiple Children Ledgers, Now Everyone Has The Same Ledger…it Has Been distributed to Everyone.
Quantum Computing And Limits Of Blockchain
So Is Blockchain A Silver Bullet To Solve All The World’s Problems? In Short, No. While Blockchain And Distributed Ledgers Have The Potential To Solve Myriad Of Our Current, Real-world Problems, It’s Also A Function Of Current, Real-world Solutions.
At The Heart Of Blockchain Are Complex Mathematical Problems That Need To Be Solved In Order To Add Legitimate Blocks To The Chain. Essentially, A Transaction To The Correct Owner Involves A “private Key”. Current Computers Do Not Have The Processing Power To Solve And Crack These Private Keys In A Reasonable Amount Of Time, Making The Bitcoin Infrastructure Virtually Hack-proof.
However, A quantum Computer operates In A Different Way From Modern Computers. Essentially, All Current Computers Operate By Using Binary Code – 1s And 0s, ‘on’ Or ‘off’. Instead Of Just On Or Off, A Quantum Computer Can Have An Infinite Number Of Values (i.e., 1, 0, 1&0, Any Number Between 1 And 0 Concurrently).The Big Difference Between Existing Computers And Quantum Computers Is The Number Of Simultaneous Calculations They Can Perform.
So, In Theory, A Quantum Computer Could Hack Bitcoin Accounts And Steal Money. While A Workable Device Is Probably Decades Away, It Is A Potential Threat To An Economy Based On A Blockchain Infrastructure.
How Blockchain Could Change The Company Of The Future
Companies Are Organized To Provide Consumers With Value. If Companies Do This Efficiently, They Grow. If They Do A Bad Job, They Go The Way Of Kodak.
When Customers Buy Goods From Businesses, They Do So On Faith. Even Large
well- Known Companies Can Make Mistakes, But Customers Believe That They Can Trust Products They’ve Bought Based On Past Experience Or Based On Reviews From Friends Or Colleagues.
When Companies Buy Goods From Other Companies, They Go Through A Similar Calculus. Larger Firms Might Have More Rigorous Protocols Around Their Supply Chains, But Ultimately, Someone Is “trusting” The Merchant On The Other Side Of The Deal. Or They “trust” That The Regulators Investigate All Market Participants To Uncover Wrong-doing.
In The Modern Era, The Best Way To Produce Goods And Services For Consumers Or Other Businesses Has Been To Form Businesses. The Modern Corporation Has Facilitated Risk-management, Knowledge Transfer And A Whole Host Of Other Activities Which Reduce The Need To Trust Others.
Ultimately, Both Business To Consumer And Business To Business Transactions Boil Down To Contracts. How They Are Written, How They Are Interpreted And How They Can Be Enforced. One Way To Reduce The Number Of Required Transactions Need To Produce A Good Or Service Is To Internalize These Transfers In The Form Of A Company. The Other Way To Operate Businesses Is To Have Better Contracts Between Parties.
In A Simple Example, A Company Who Needs To Execute A Marketing Campaign Can Either Hire An Agency Or Produce The Campaign In-house. The Same For Legal Or Other Services. However, The US Auto-industry Might Be A Sign Of Future Manufacturing Especially In A Blockchain Enabled Environment.
Ford And GM Don’t Manufacture Cars. They Manage Sprawling Supply Chains Of Specialized Firms Which Produce Inputs They Need To Assemble The Final Product. The Future Could See The Growth Of decentralized Autonomous Organizations. In This Possible Future, People Or Small Firms Specialize In Niche Fields And Sell Their Services In A Marketplace In Near Real-time. There’s No Need For Companies In The Traditional Sense. Of Course, This Has Many Simplifying Assumptions Like Adequate Regulation To Protect Consumers And The Like.
Smart Contracts
If The Contracts Themselves Contain Features That Auto-execute, Then We Waste Less Time Approving Vendors. Blockchain Allows A Contract To Have A Payout Feature Only If The Task Is Completed To Specifications. Money Would Be Held In Escrow Or Within The Contract Itself And The Proof Of Completion Would Trigger The Payment.
Smart Contracts still Have The Potential Of Fraud Or Collusion, But It Becomes Harder And Harder To Game The System. Contracts, Including Employment Contracts, Help Us Organize Ourselves.
In The Same Way, A New System Where Each Individual Participant “trusts” Who They Are Dealing With Directly Could Result In Far More Freelancers And Contractors Than Actual Employees.
Is This All Science Fiction?

Source: Wikimedia: Creative Commons
Talking About The Future Is Always Fraught With Challenges. In 1900, People Predicted That Fireman Would Have Wings And Put Our Fires From The Air. Outside Of A Hollywood Blockbuster, This Clearly Has Not Happened.
So Let’s Turn To What Companies Are Doing Right Now With Blockchain To Have A Glimpse Into What We Should Expect In The Next 5 Or 10 Years.
- Monetary Authority Of Singapore – MAS Has Formed A Partnership With The R3 Blockchain Consortium To Develop A System Of Inter-bank Funds Transfer.
- IBM-Bluemix Garage – At The 2016 Singapore Fintech Festival, IBM Unveiled An Initiative To Help Financial Services Companies With Their Compliance Requirements Using Blockchain. Know-Your-Customer Or (KYC) Is A Big Pain Point In Banking And Has Obvious Similarities With Employee On-boarding.
- Nasdaq – Allows Private Companies To Issue Shares Using Blockchain To Power The Transaction.
- Philips – Has Partnered With Start-ups Gem And Tierion In A New Project. Although Details Of The Initiative Have Not Been Disclosed, It Will Likely Involve Medical Records. Tierion Provides A Service To Use Blockchain As A Way To Verify Any Bit Of Data, File Or Business Process.
- Toyota – The Financial Services Arm Of Toyota Is Looking At Ways To Track Assets In The Car Production Process Or Enable Connected Cars To More Easily Communicate With Their Owners.
The Potential Impact Of Blockchain On Employment Screening
With More Trust Between Buyers And Sellers, One Implication In The Future Is That Hiring Becomes More Transparent. Imagine A Central Repository That Is Opt-in And Hack-proof. Anyone Accessing The Database Can Be Assured That The Data Is Robust And True. Anyone Who Chooses To Operate Outside Of The Database Would Be Automatically Subject A Greater Level Of Scrutiny.
In This Fictional World, There Is No Need For A Third-party Company To Screen A Candidate’s Work History And Professional Credentials. A Company Would Pay A Subscription To Access The Database Directly And Simply Review A Prospect Against Their Profile In The Database.
Banks Are Currently Exploring A Similar System To Share Data On An As-needed Basis. The Person Who Owns The Data (the Bank Customer Or The Job Applicant) Can Decide Which Data Is Visible To Which Participant. For Example, I Could Specify That Employers Can View The University I Attended, The Year I Graduated And Degree Earned. Alternatively, If An Employer Only Wanted A Candidate With A X Years Of Experience, I Could Have The Ability To Phrase The Question To Be Yes Or No (I Have A Relevant Experience Without Specifying The Year I Graduated).
The World Of Tomorrow Will Have To Strike A Balance Between Having Safeguards And Protecting Consumer/job Applicant Data And Operating More Efficiently. Given The Way Millennials Are Prone To Share Everything And Allow Facebook Open Access To Virtually All Apps, It’s Unlikely That Disclosure And Opt-in Will Be A Major Issue In The Future.
Making Verification Easier
One Organization That Is Already Using Blockchain To Warehouse Earned Degrees Is The Holberton School – A California Computer Programming Institution. Degrees Are Transferred To Graduates Via Blockchain Where They Are Secure And Authenticated.
If All Academic Institutions Stored Their Degrees In A Similar Fashion, Employers Would Need Only Access That Database To Verify An Applicant’s Credentials. The Same Could Be Done For Professional Qualifications Or Continuing Education.
Earlier In 2016, Recruit Technologies Announced A Partnership With Ascribe Where They Will Develop Blockchain Powered “Certificates Of Authenticity”. Work Is Underway To Create A Database To Verify Resumes Of Prospective Job Applicants.
In The Meantime, You Still Need Screening Companies
Quite Often, When Professionals Talk About The Intersection Of Human Resources And Technology Or “hrtech”, They Talk About Chatbots Or (“AI”) artificial Intelligence.
In Part, This Is Because It’s The Most Obvious, Real-world Application That Impacts Us Today. There’s Really No Way To Understate The Rapid Change That Is Currently Underway.
Quite Likely, You’ve Interacted With Artificial Intelligence This Week And Hadn’t Realized It. From Chatbots That Power Some Customer Service Portions Of Websites, To The Intelligent Algorithm That Runs Siri,
technology Is Running In The Background More And More.
While A Brave New World May Be Quickly Upon Us, The Reality Is That Some Of The Today’s Thorniest Problems Still Need Human Attention. You Need A Person To Help Understand The Nuance Of The Specific Question You Are Trying To Answer.
You Get What You Screen For
Liz Ryan Of The Human Workplace Wrote An Excellent Piece About The Need For proper Employee Screening. It Was Written In 2008 But Is Still Relevant Today. She Describes An Interaction With A Manager Who Had A Poor Disposition And Terrible Demeanor. You Can’t Screen For Everything, But You Should Know What An Applicant Will Need In Order To Excel In A Role.
“On The Drive Home, I Remembered That The Copy Shop Uses Extensive Testing In Its Pre-employment Screening. I’ve Seen About Every Big-company Pre-employment Test There Is (thanks To Camera Readers And Others Who Know Of My Geeky Interest In Such Things), And I’ve Seen This Copy Shop’s Tests — And They’re Extensive.
They’re Taken Online At The Start Of The Application Process. They Measure A Job Seeker’s Math And Analytical Skills. They Measure His Or Her Logical Skills.
What They Don’t Touch Is Interpersonal Communication — No Questions Like, “Which One Of These Responses Is The Best Choice When A Customer Is Unhappy With Our Service?”
When You Look At Your Recruitment Process, Does It Sound Like The Scenario Above? If You’re Looking For That Personal Touch To Help You In The Recruitment Process, Then Please Reach Out To Us At info@checkbox.sg.




